Lipids and Nutraceuticals March April 2024
Laurence Eyres FNZIFST
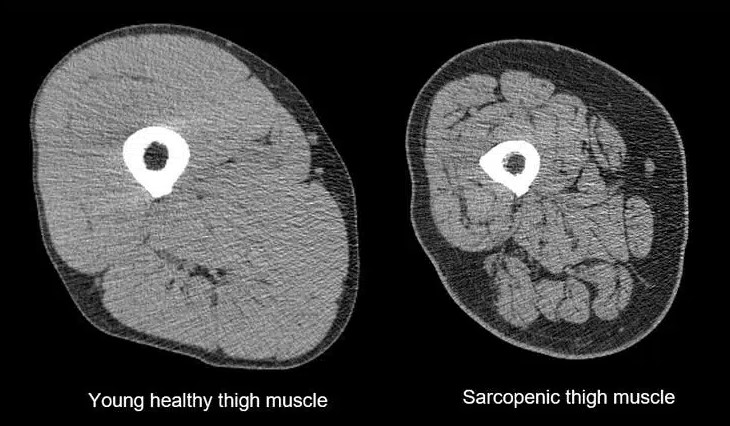
Sarcopenia for the senior readers.
Medicine describes Sarcopenia as:
1) Loss of muscle mass
2) Loss of muscle strength
3) Loss of muscle function When it comes to sarcopenia and nutrition, enough protein and amino acids are needed for muscle synthesis and maintenance. The recommended dietary allowances are:
(RDA) is 0.8 grams of protein /Kg of body weight each day, and 2.14.
grams/Kg/day of amino acids. However, as we age, we need.
more than these values due to malabsorption of proteins and amino
acids. A healthy range would be 25-30 grams of high-quality protein.
Food Supplements
β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) is a metabolite derived from leucine and its ketoacid alpha- ketoisocaproate.
It comes as a white powder which is bitter to taste but I sprinkle on morning cereal. Leucine has a role in regulating protein synthesis in muscle cells, and HMB seems to be a key active metabolite in such regulation. HMB has been shown to modulate muscle protein degradation by inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway, HMB is widely used as an ergogenic supplement by athletes and bodybuilders, usually combined with exercise training, to increase muscle mass and strength. Some studies have explored the role of HMB in chronic diseases associated with muscle wasting (cancer, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
Bone Abstracts (2016) 5 P387 | DOI: 10.1530/boneabs.5. P387
Vitamin D update
A Deficiency is strongly linked to increased risk for a multitude of diseases, several of which have historically been shown to improve dramatically with either adequate UVB exposure to the skin, or to oral or topical supplementation with vitamin D. These diseases include asthma, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, rickets, and tuberculosis. In a recent USA hospital trial, three patients with psoriasis showed marked clinical improvement in their skin using 20,000 to 50,000 IUs/day. Analysis of 777 recently tested patients (new and long-term) not on D3 revealed 28.7% with 25-hydroxyvitaminD3 (25OHD3) blood levels < 20 ng/ml, 64.1% < 30 ng/ml, a mean 25OHD3 level of 27.1 ng/ml, with a range from 4.9 to 74.8 ng/ml.long-term supplementation with vitamin D3 in doses ranging from 5000 to 50,000 IUs/day appears to be safe.
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 May: 189:228-239.
Omega-3
A daily intake of between 1 and 2 g/day of Ω-3 EPA + DHA must achieve an Ω-3 index > 8%, and an individual’s ultimate dose is dependent on their background diet of other fats, specifically omega-6 fatty acids.
There is, however, clear evidence from multiple studies that higher doses of Ω-3 (2–4 g/day of EPA + DHA) appear to be safe and to reduce CVD events in multiple CVD populations, which warrants further study to conclusively determine the potential benefits of this safe, inexpensive, and well-tolerated therapy.
Nutrients. 2021 Jan; 13(1): 204. online 2021 Jan 12. doi: 10.3390/nu13010204
Plasmalogens of mussel
Marine and freshwater two-part shell mollusks, in which both valves are typically symmetrical along the hinge line, belong to the class Bivalves (they are also under names Pelecypoda, and/or Lamellibranchia). The words “clams, mussels, scallops and oysters” have no real taxonomic significance in biology, but in cookery these words have definite significance, and are associated with savoury food (Fernandez, Garcia, Asensio, Rodriguez, & Lobo, 2001). Edible bivalves, clams and mussels are marine species with a few well-known freshwater representatives. They are widely used as nutriments around the world (Ackman, 2000), and they are present at food market for about one hundred years.
Growing evidence suggests that ethanolamine plasmalogens (PlsEtns) a subtype of phospholipids, have a close association with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Decreased levels of PlsEtns have been commonly found in AD patients and were correlated with cognition deficit and severity of disease. Limited studies showed positive therapeutic outcomes with plasmalogens interventions in AD subjects and in rodents. The potential mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of PlsEtns on AD may be related to the reduction of γ–secretase activity, an enzyme that catalyses the synthesis of β-amyloid (Aβ), a hallmark of AD. Emerging in vitro evidence also showed that PlsEtns prevented neuronal cell death by enhancing phosphorylation of AKT and ERK signalling through the activation of orphan G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) proteins.
Saffron
The precious spice comes from the stigma of the crocus sativus - a purple flower which blooms for just a few weeks in the autumn – and it sells for $57,000 a kilo now. The painstaking autumn harvest is, however, counted in grams.
There are many challenges extracting the brightly coloured stigma during harvest including keeping bees away and dealing with morning dew.
Olive oil
In a recent review published in the Nutrients, a group of authors explored the therapeutic potential of oleuropein (OLE) and hydroxytyrosol (HT) from olive oil as novel antioxidants in the treatment of neuroblastoma (NB), addressing challenges such as recurrence and drug resistance.
NB, the most common extracranial tumour in young children, originates from nerve tissues and is challenging due to recurrence and drug resistance.
Olive oil’s OLE and HT, rich in antioxidant properties, appear as potential treatments, promising lower toxicity and harnessing the Mediterranean Diet’s (MD)’s cancer-preventive benefits.
Further, in vivo studies and clinical trials are essential to confirm their therapeutic efficacy and safety in NB cases.
Macular Carotenoids, Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Safety, Efficacy and Bio-Delivery.
Eye health has appeared as a serious issues of global health concern with a decline in quality of life in an aging population and rise in the number of associated morbidities and mortalities. The number of incidences of ophthalmic diseases including cataract, Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD), glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy have increased alarmingly over the last few decades leading to a gradual and progressive loss of eyesight in addition, the dry eye disease has increased the burden of these debilitating pathologies. Various ocular manifestations have also been revealed in young adults as an aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic partly because of the virus itself. One of the chief reasons for vision impairment is oxidative damage inflicted to photoreceptors in rods and cone cells by blue light as well as UV radiation. The situation has been aggravated by an unprecedented rise in screen-time during the COVID and post-COVID era. Lutein and Zeaxanthin are carotenoids with proven roles in aid of eye health by virtue of their antioxidant properties and protective effects against photobleaching of retinal pigments, age-linked macular degeneration, cataract, and retinitis pigmentosa. These molecules are characterized by their characteristic yellow-orange coloured pigmentation and are found in significant amounts in vegetables such as corn, spinach, broccoli, carrots as well as fish and eggs.